The Present and Future
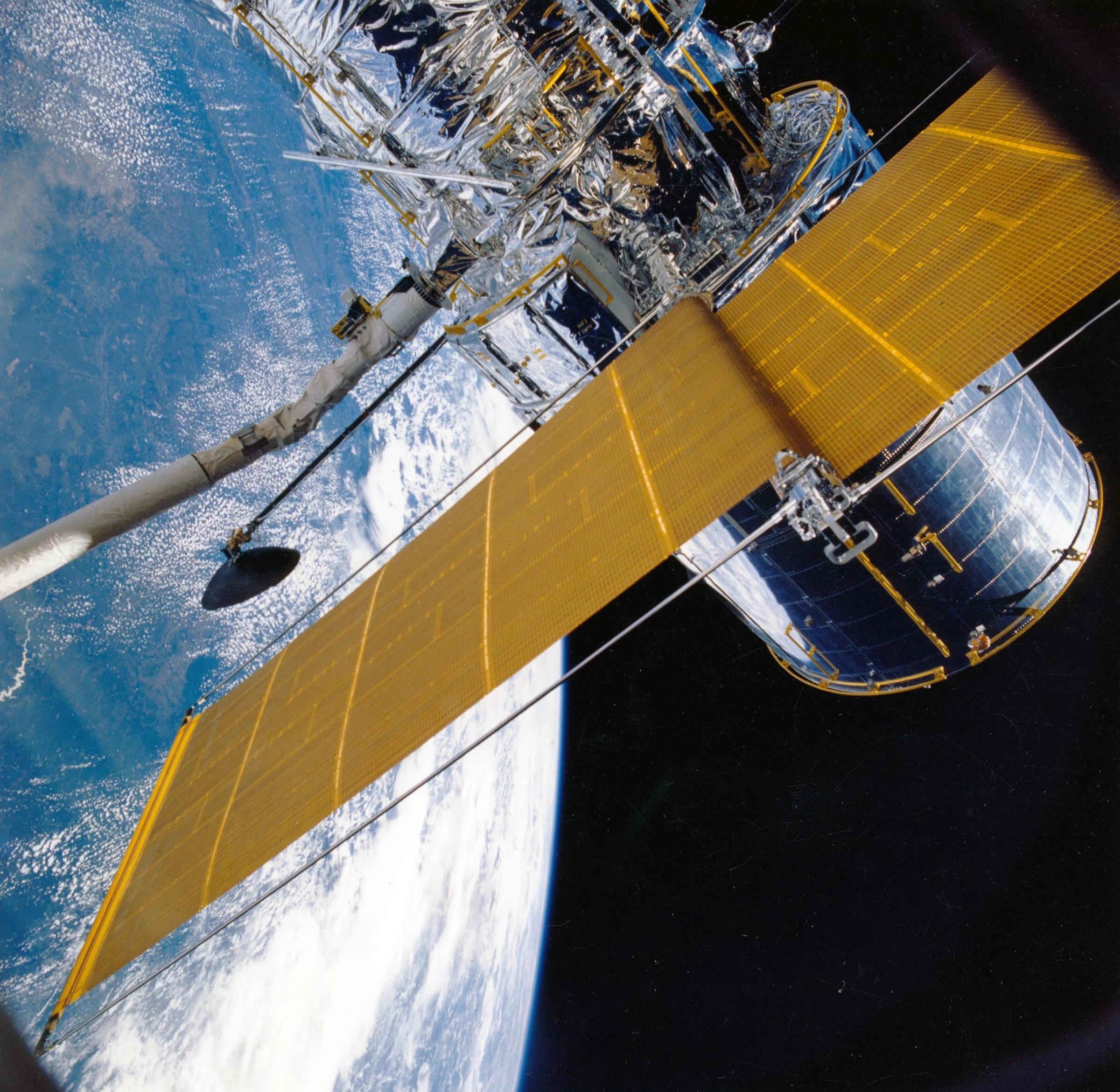
The present state of space exploration is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field, with a growing number of nations and private companies launching missions and developing new technologies. In recent years, there have been numerous high-profile missions to Mars, including the successful landing of the Perseverance rover in February 2021, as well as continued efforts to study other planets and celestial bodies. Private companies such as SpaceX are also making significant strides in space exploration, with plans to eventually establish a human settlement on Mars. Additionally, the International Space Station continues to serve as a platform for scientific research and experimentation, with regular crew rotations and resupply missions. As space exploration continues to progress, it has the potential to provide valuable insights into the nature of our universe and the origins of life.
IMAGE
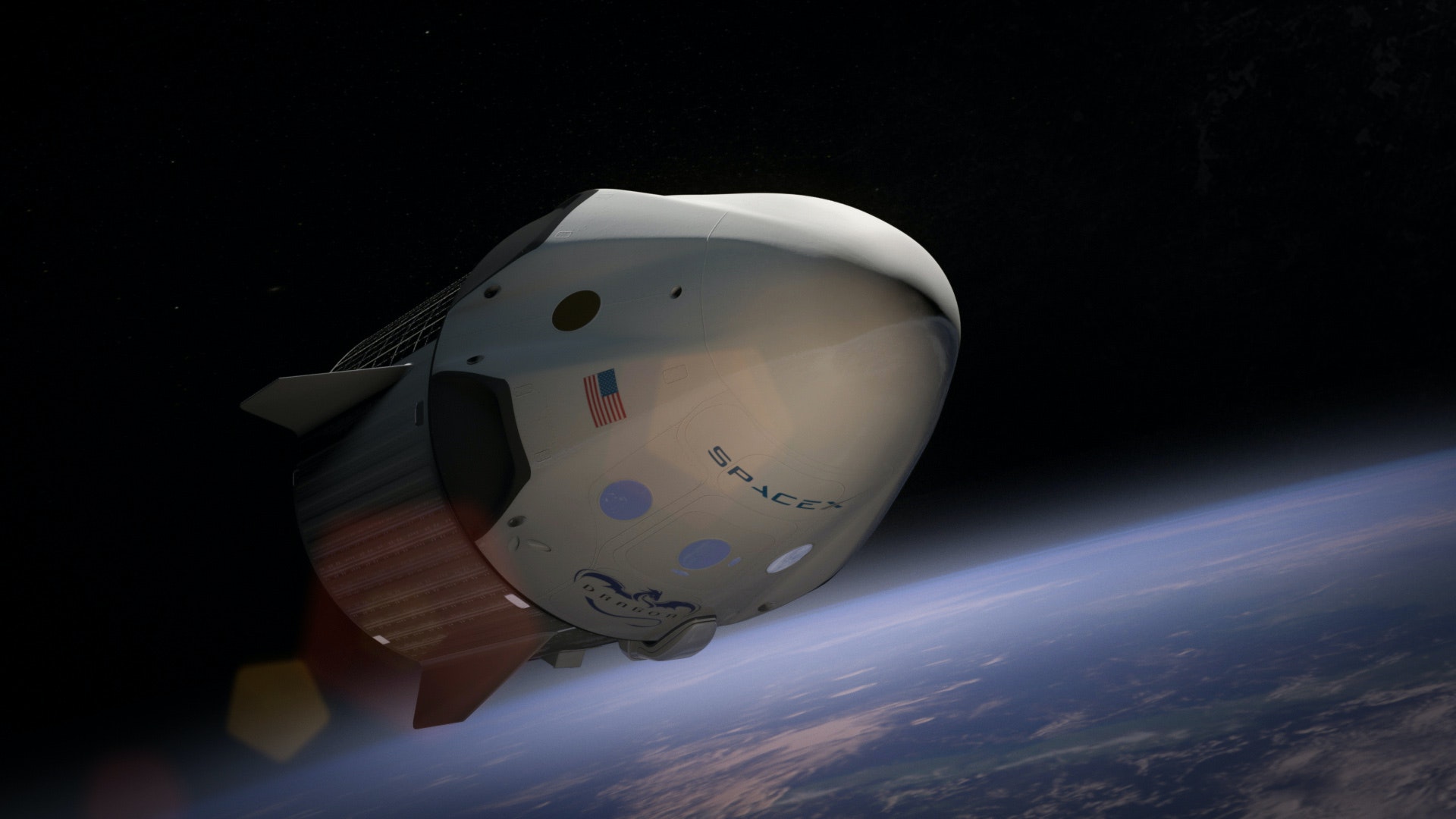
SpaceX : Man on the Mars
SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, has an ambitious mission to establish a permanent, self-sustaining human settlement on Mars. The company envisions a multi-stage approach to achieving this goal, beginning with the development and launch of its Starship spacecraft. This fully reusable rocket and spacecraft system is designed to carry up to 100 people at a time and has the capability to transport both crew and cargo to the Red Planet. SpaceX plans to use Starship to launch several uncrewed missions to Mars to test the technology and demonstrate its ability to transport cargo and equipment. The ultimate goal is to establish a sustainable, long-term presence on the planet, with the first crewed missions potentially taking place in the mid-2020s. SpaceX's vision for Mars colonization is seen as a major step forward in space exploration and could have significant implications for humanity's future in space
SOURCE: NASA

