Parkinson's Disease is a progressive disease that occurs in two main parts of the brain, the substantia nigra and the basal ganglia. The substantia nigra controls the dopamine throughout the body that is in charge of planning and controlling movement. Scientists don't know why, but in some individuals, the dopamine producing nerve cells die off. When around 80% of these have died, symptoms of Parkinson's are experienced. The basal ganglia are also in charge of motor control. and are affected by Parkinson's as a result.
Impulses travel from neuron to neuron throughout the body to the muscles, which react to the signals being sent, causing movement. If dopamine producers are over or under stimulated, the body experiences rigidity, tremors, and other symptoms of Parknson's. To compensate for the lack of dopamine, bodies often make extra glutamate to act as another neurotransmitter.
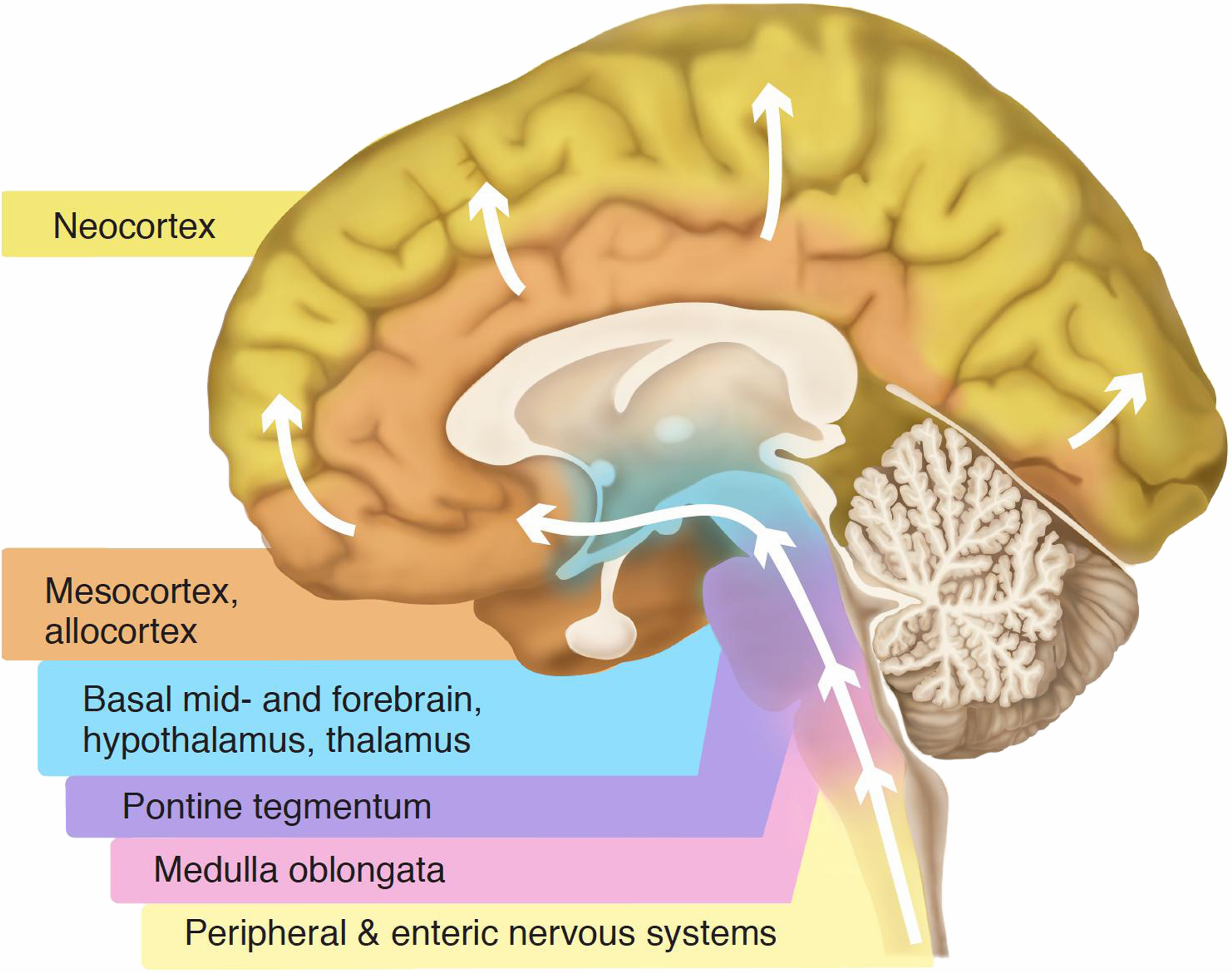
Braak Staging: Yellow represents the origin of Parkinson's pathology. Pink/purple represent Stages 1 and 2. Blue represents Stages 3 and 4. Orange represents Stage 5. Yellow represents full neocortex engagement and Stage 6 from wikipedia.org. CC-BY
