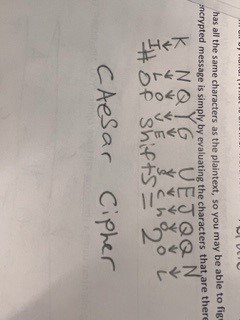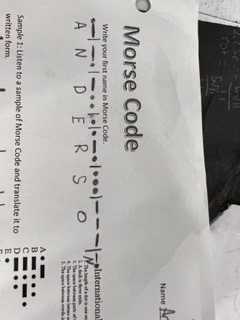Home Page
Ethics
Cryptography
Security Principles
WebSecurity
Training
Cryptography
Cryptography has been able to evolve to such a great level over time. Classis ciphers like the Caesar cipher have come to be useless with modern day technology, compelling cryptographers to develop much more complex ciphers. An example of classic Ciphers that used to be commonly used is the Caesar cipher. This cipher is based off several shifts in the alphabet leading this cipher to be basic and leading any slightly skilled person decrypting the message would be able to pick up and decode the message. As well as the person who is receiving the message would have to know the number of shifts in the alphabet. Ciphers have evolved now to things like public key encryption which involves a much more advanced level of decryption to be able to crack the cipher. Public key encryption is where there is a public key which allows users to send messages into someone’s inbox but only the receiver that has the private key/password would be allowed to read the messages sent. You can look at this as almost a 2-way mailbox. Imagine public key encryption as a mailbox. There is one entry way for anyone to just walk up and drop a message or letter into but there is usually a lock on the mailbox only the receiver must be able to open it and read the messages. This is vital for information, so people are not able to just read your messages. Public key encryption protects a user's privacy.
Caesar Cipher
The Caesar cipher is controlled by a certain number of shifts in the alphabet. Every character in the word is shifted a certain number of times in the alphabet. The whole point of the Caesar cipher is to allow the receiver to know the number of shifts the letters are shifted in the alphabet so the random message sent can come out to something not so random.
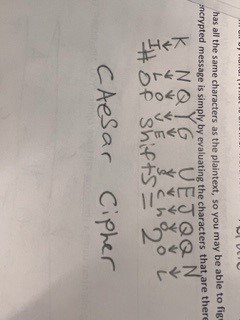
Morse Code
Morse code is a cipher where one can turn a message into a pattern of dots and dashes. In morse code if a person was to intercept a message before people had cracked the code when one was to intercept a message being sent in morse code it would leave one to believe it is a message of nonsense. One would have to have the key of how the patterns of dots and dashes corresponded with what letters to be able to decrypt a message.
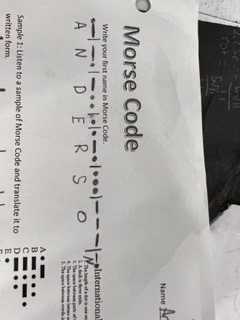
Salting and Hashing
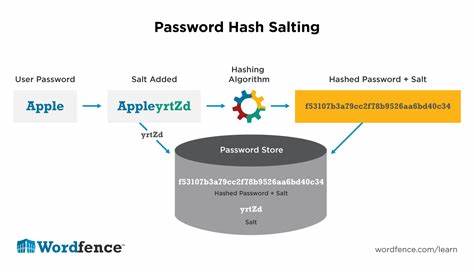
Salting and Hashing is a vital aspect of cyber security. When databases lack salting and hashing in their software their information like passwords etc. become much more vulnerable to hackers. Hashing creates a theoretically unreversible encryption also known as a 1-way function. This creates a level of security for users based off the fact that if a hacker did break into a database the information given would be hashed and unreadable. Salting just adds another extra layer of security due to the fact that if passwords are the same the hashes in the database would be identical as well. A hacker might be able to use that information and look through rainbow tables because if passwords are identical, they are most likely more common passwords as well. Salting adds on a unique set of characters that adds onto the hash making no 2 hashes alike there for deleting the aspect of identical hashes.
Website Created by Anderson Howard, student at the John Carroll School